When a crisis hits, be ready to switch to teleworking. That is just one of the lessons COVID-19 has taught companies all around the world. Remote working should go hand in hand with extra cybersecurity measures – here’s how to achieve them.
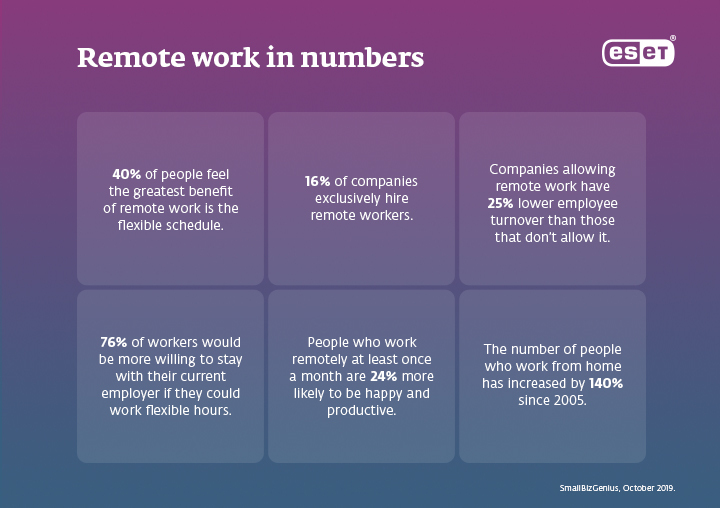
When the COVID-19 pandemic hit, companies around the world transitioned to remote working almost overnight. This presented a big challenge for many small to medium-size businesses (SMBs), especially those that had no prior experience with flexible workspaces and digitalization. Many struggled to ensure device and network security as well as business continuity. Below are the lessons learned and practical steps that SMBs should consider to meet the demand for flexible workspace options moving forward.
1. Equip all employees technologically as well as psychologically
Along with technology, psychology plays a crucial role in teleworking. If your employees are struggling with work morale, try to share some tips on how to be productive at home and how to adopt a good routine.
For some employees, the remote office might be their first encounter with new digital solutions. How can you ensure that the new online setup will be a success for employees? The key ingredient is motivation: “You need to know your employees, their values and attitudes, and approach them accordingly. People need space for self-realization and they should be assigned tasks they enjoy. Thanks to that, they will work as best they can and use new tools enthusiastically,” says Ján Kulich, IT manager at ESET.
2. Focus on extra endpoint security
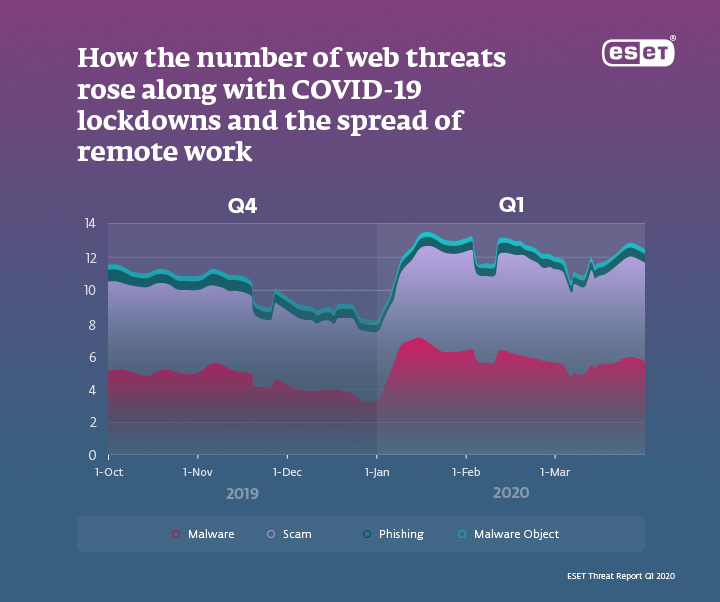
Outside of a business network, devices are much more vulnerable to cyber attacks and employees are more likely to fall victim to hackers. The COVID-19 experience says it all: according to the recent ESET Threat Report Q1 2020, the number of fraudulent websites blocked in Q1 2020 increased by 21% compared to Q4 2019. Those threats included various types of malware, scam and phishing websites, many of which leveraged coronavirus-themed content and domain names to attract as many visitors as possible.
Therefore, make sure all devices are protected with an advanced endpoint security solution that has a web access protection module to detect and block websites with malicious content. You will also appreciate using an endpoint management solution that can allow you to configure and fix problems remotely, as well as receive immediate notifications of detected anomalies. If someone tries to hack your employees’ devices, a quick reaction can save you a lot of trouble.
TIP: Divide your employees into different groups and create a standardized environment that will allow you to make changes and updates to all devices at once.
Next, make sure your employees know how to create a strong password and use multi-factor authentication. This will prevent uninvited guests from accessing important documents as well as from using stolen passwords to take over employees’ accounts. Protecting accounts with strong passwords might sound like a basic recommendation, but as studies have shown, the most commonly used passwords still tend to be “123456,” “111111” or simply “password.”
Cyber awareness matters, especially when working remotely. Remind your employees not to leave their devices unattended in public places and to log out when not using their devices. This can also help prevent children from sending funny but inappropriate emails to colleagues and bosses or changing your settings.
3. Guarantee accessibility, but don’t forget to check who gets what and where
Maybe your employees only need to use cloud services and email – resources that can be accessed easily and without any special security measures. But what if they need to access your internal business network? In this case, a VPN (virtual private network) connection is a must. Among other benefits, it prevents man-in-the-middle attacks that can seriously threaten your security.
Preferably, employees should only use company devices, even when working remotely, and you should be aware of all additional external devices they use, whether hard drives, USB disks or SD cards. If they need to use private computers, equip your employees with the same endpoint security solutions that you provide for company devices.
Keep in mind one simple rule: the more material your employees download from the internet, the higher the probability an infected file will find its way onto their computers. Hence, limit the ability to download, copy and store data.
Devices can also be compromised by visiting untrustworthy websites or clicking on fraudulent links. Having no colleagues behind their back, employees are more likely to take risks when working from home. One possible way of limiting access to potentially harmful content is using virtual machines – it’s a more sophisticated solution, but in the long run it can improve security for remote workers.
Some of the most common attacks on remote workforces
Phishing attacks: A form of social engineering attack in which the criminal impersonates a trustworthy entity while requesting the victim to click on a malicious link or visit a dodgy website.
Scams: Can range from fake e-shops to frauds and fake offers. During COVID-19, typical scams have included fake e-shops selling medical equipment that the customer never received or that were of substandard quality.
Business Email Compromise (BEC) attacks: a bogus demand sent by a bad actor asking for the urgent transfer of funds, without the ability to validate the request in person.
Man-in-the-middle attacks (MITM): An attack where the hacker intercepts the communication between two parties without being noticed. Cybercriminals can monitor and control conversations as well as file exchanges.
Malware attacks: Any attack that aims to harm, spy on or steal from devices by installing trojans, backdoors, spyware, coinminers and other malware. Particularly harmful is ransomware, which encrypts user data and requires the payment of a ransom that may or may not lead to the restoration of the encrypted data.
4. Focus on effective communication
When working off-site, communication can get tricky. Therefore, make sure to regularly ask for employee feedback on how happy they are with the new working reality and use reliable apps that make it easy to stay in touch virtually. You can also implement useful collaborative tools that help organize teamwork and allow employees keep track of what colleagues are doing.

As you start integrating new digital solutions, some employees may need thorough guidance and many questions will be posed. Answer all of them patiently, explaining the benefits of remote working, and, if possible, set up a dedicated email address where employees can send their queries.
Your initial efforts to digitize the workplace can be difficult, but it’s well worth the effort. In the months and years to come, flexible workplaces will not only be a competitive advantage that can attract talent, but also a necessity for businesses to survive any future crises.






